Project 1: Epigenetics of Castration-resistant Prostate Cancers
- Highlights:
- HOXB13, a homeodomain containing transcription factor, is linked to aggressive Prostate Cancer (PCs). However, to date its critical epigenetic regulators and effectors in PC metastasis remain largely unknown. We uncovered that the BET bromodomain protein family, including BRD4, is an epigenetic regulator of HOXB13. BRD4-HOXB13 inturn regulate unique mitotic transcriptional networks that is Androgen receptor independent and upregulated during metastasis. To target the pro-proliferative HOXB13 driven transcriptional networks, we utilized dual activity Bromodomain-kinase inhibitors to block transcription of the HOXB13 gene and were able to inhibit the growth of metastatic CRPC xenograft tumors.
- Barashi, NS*, Li T, Angappulige DH, Zhang B, O’Gorman H, Nottingham CU, Shetty AS, Ippolito JE, Andriole GL, Mahajan NP, Kim EH, and Mahajan K*. Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Suppressed Epigenetic Regulator HOXB13 Show Lower Incidence of Prostate Cancer Development. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 2;16(1):213. PMID: 3820164
- Angappulige DH, Mahajan NP, and Mahajan K*. Epigenetic Underpinnings of Tumor Immune Dynamics in Prostate Cancer Immune Suppression. Trends in Cancer, 2024.
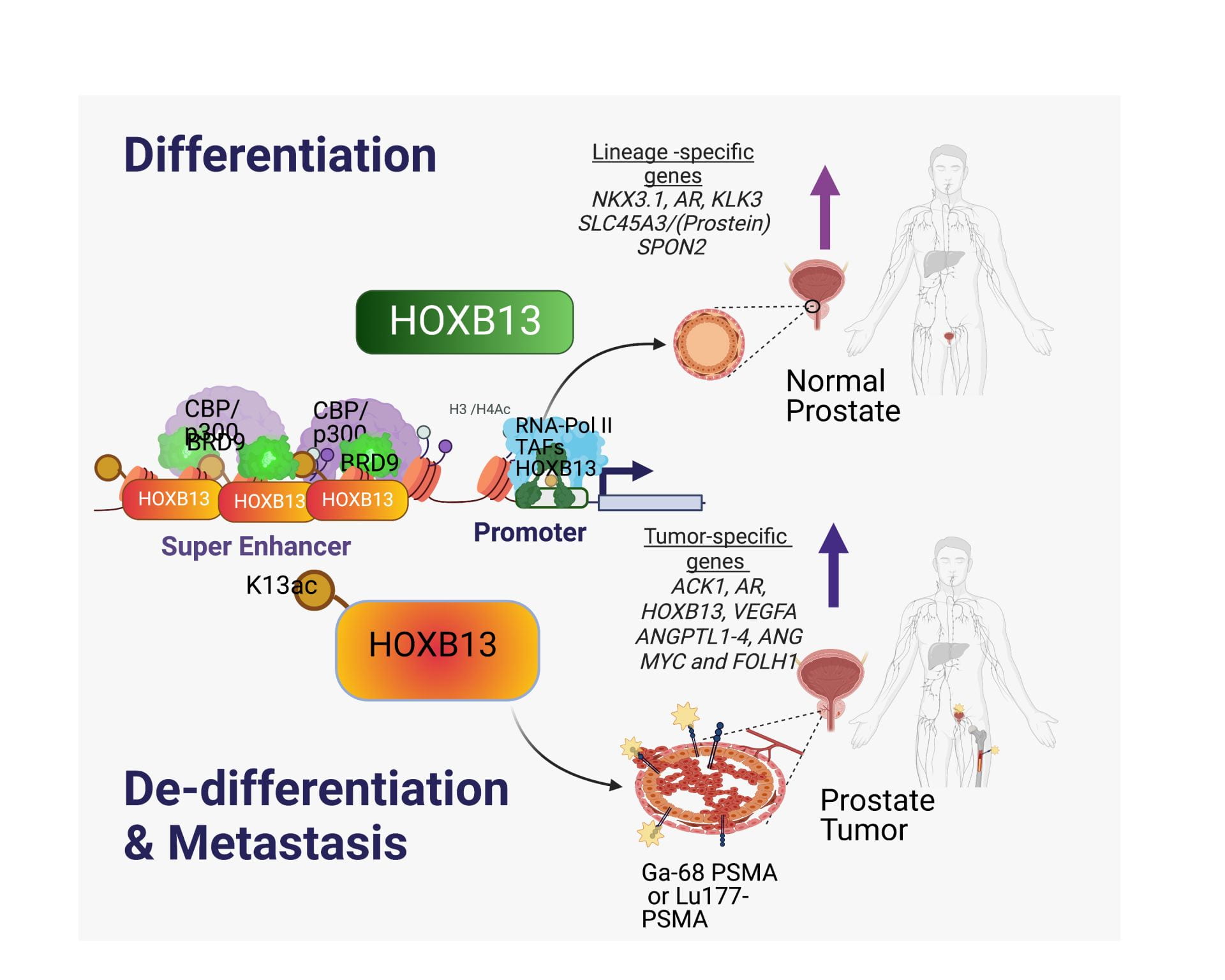
In a new finding, we uncovered a novel gain-of-function lysine (K)13 acetylation in HOXB13 mediated by the histone acetyl transferases, CBP/p300. By employing acK13-HOXB13 ChIPs in matched human normal and prostate tumors, we identified ‘tumor-specific SEs’, including SEs at the ACK1 and FOLH1 (PSMA) genes, which code for actionable targets. Thus, ‘acK13-HOXB13’ and ‘tumor-specific SE regulated genes’ are clinically relevant biomarkers to screen lethal PCs. Targeting prostate cancers expressing Super Enhancer-regulated genes at onset may be the key to preventing the development of CRPC in men diagnosed with the disease.
Nguyen D#, Yang W#, Renganathan A, Weimholt C, Angappulige DH, Nguyen T, Sprung R, Andriole GL, Kim EH, Mahajan N, Mahajan K#* Acetylated HOXB13 Regulated Super Enhancer Genes Define Therapeutic Vulnerabilities of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, July 18, 2022, PMID: 35849143DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3603.
We demonstrate that HOXB13 correlates with PSMA expression and PSMA PET SUVs at the mRNA and protein levels. Our study suggests that the PSMA PET findings may reflect oncogenic HOXB13 transcriptional activity in PC, thus potentially serving as an imaging biomarker for more aggressive disease.

Angappulige DH, Barashi NS, Pickersgill N, Weimholt C, Luo J, Shadmani G, Tarcha Z, Rayamajhi S, Mahajan NP, Andriole GL, Siegel BA, Kim EH, and Mahajan K* Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen-Targeted Imaging and its Correlation with HOXB13 Expression. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 2024 . jnumed.123.267301;
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.123.267301
Project 2: Characterization of novel small molecule inhibitors for the treatment of lethal prostate and breast cancers
- We developed (R)-9b, a small molecule inhibitor that targets ACK1, a tyrosine kinase that is significantly upregulated in castration-resistant prostate cancer. By phosphorylating histone H4 at tyrosine 88, it regulates Androgen receptor transcription and promotes Enzalutamide and abiraterone-resistant prostate cancer growth. Our research revealed that AR is modified at lysine 609, located in the DNA binding domain (DBD), in Enzalutamide treated cells. Through its control of AR phosphorylation at Y267, ACK1 regulates AR acetylation at K609. Our studies reveal that ACK1 plays an important role in the development of prostate cancer drug resistance.
- Mahajan K, Malla P, et. al., ACK1/TNK2 Regulates Histone H4 Tyr88- phosphorylation and AR Gene Expression in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. PMID: 28609657 Cancer Cell, Jun 12;31(6):790-803. 2017.
- Sawant M, Mahajan K, et. al., Chronologically Modified Androgen Receptor in Recurrent Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer and its therapeutic Targeting., Science Translational Medicine, 2022, Jun 15;14(649):eabg4132. PubMed PMID: 35704598.
- Sridaran, D., Chouhan, S., Mahajan, K.# et al. Inhibiting ACK1-mediated phosphorylation of C-terminal Src kinase counteracts prostate cancer immune checkpoint blockade resistance. Nat Commun 13, 6929 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34724-5
Project 3: Role of lineage-specific long non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer development, progression to metastasis and resistance to anti-androgens
- Recently, the contribution of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the pathogenesis of prostate cancers has acquired prominence as they are known to epigenetically regulate the function of critical tumor promoting transcription factors. Bishop et al have reported upregulation of PD-L1 in dendritic cells in Enzalutamide resistant patients and in pre-clinical models of ENZ resistance. It is unclear whether specific factors aberrantly expressed in CRPCs simultaneously modulate castration resistance as well as immune regulation to promote lethal disease. Recently, reports indicate that that BET-bromodomain epigenetically regulate PD-L1 expression in ovarian cancers. BET inhibition with the prototype inhibitor JQ1 promotes anti-tumor immunity by downregulating PD-L1 expression in both immune cells and ovarian tumor cells, and in addition increases CD8+cytotoxic T cell activity to limit ovarian tumor progression in syngeneic mouse models. We are characterizing several new long non-coding RNAs for their roles in immune regulation.
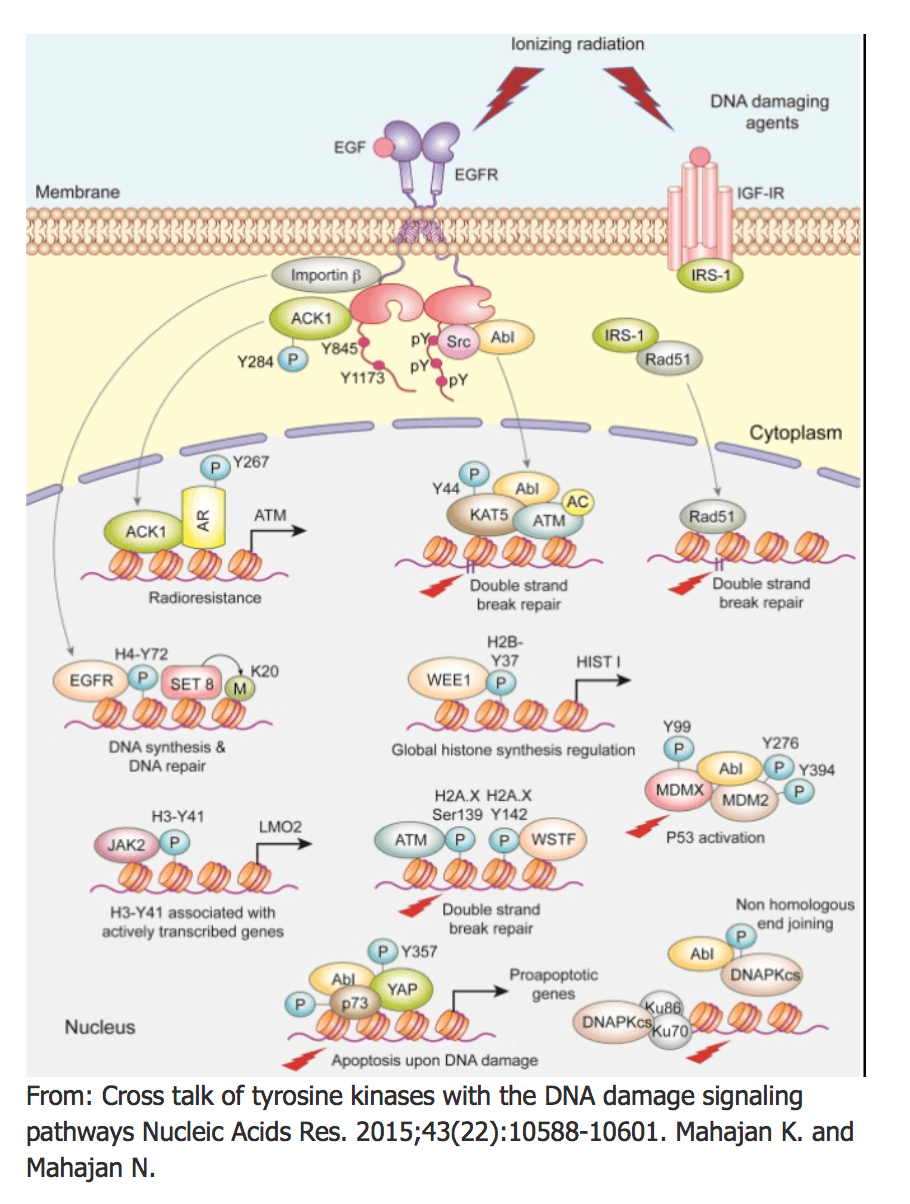
- Mahajan K* and Mahajan NP. Cross talk of Tyrosine Kinases with the DNA Damage Signaling Pathways. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(22):10588-601, 2015.